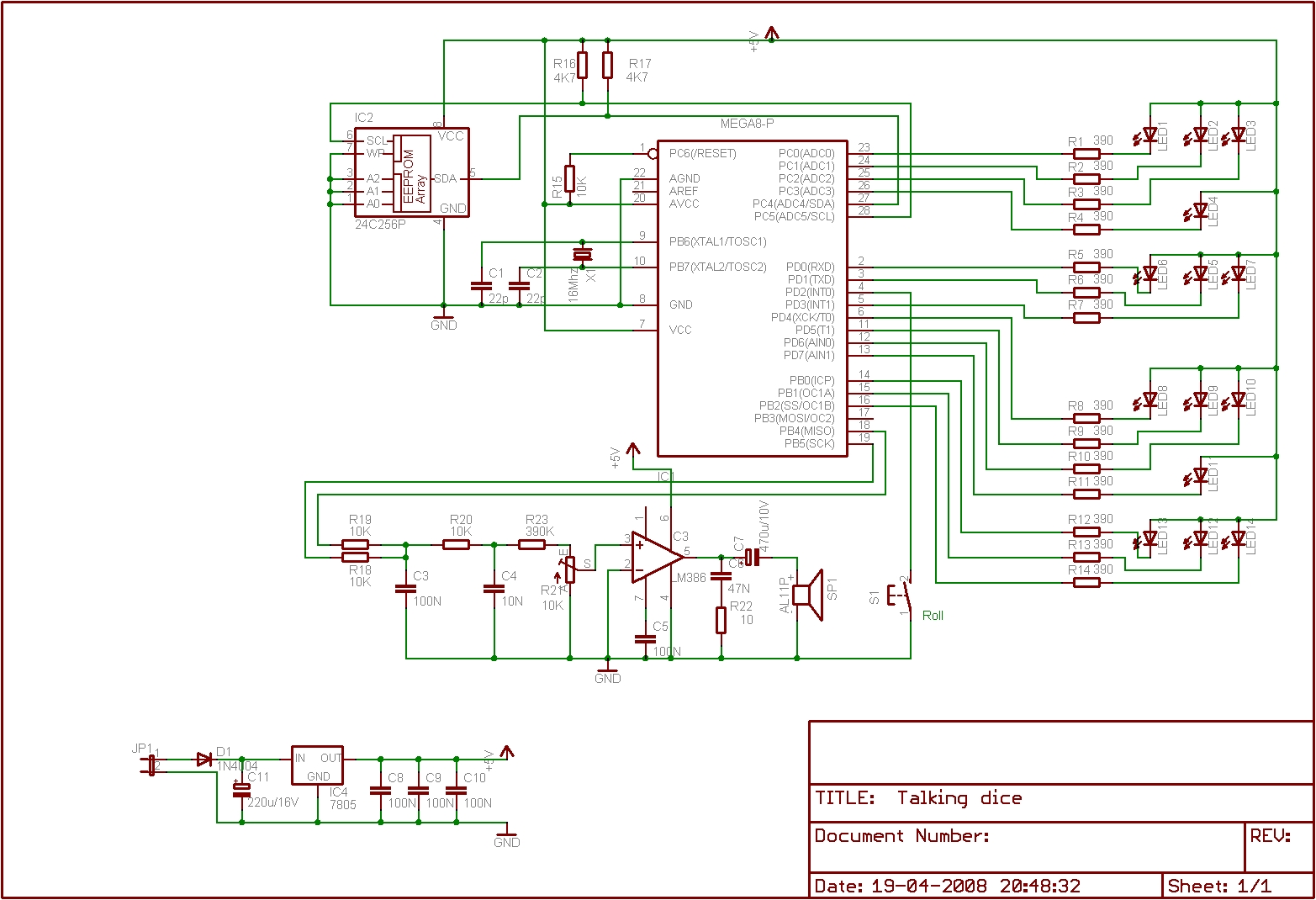
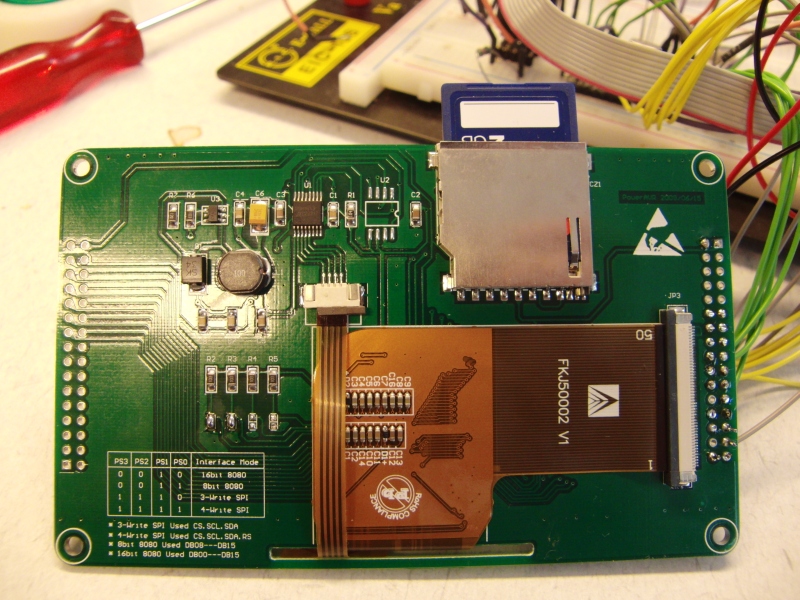
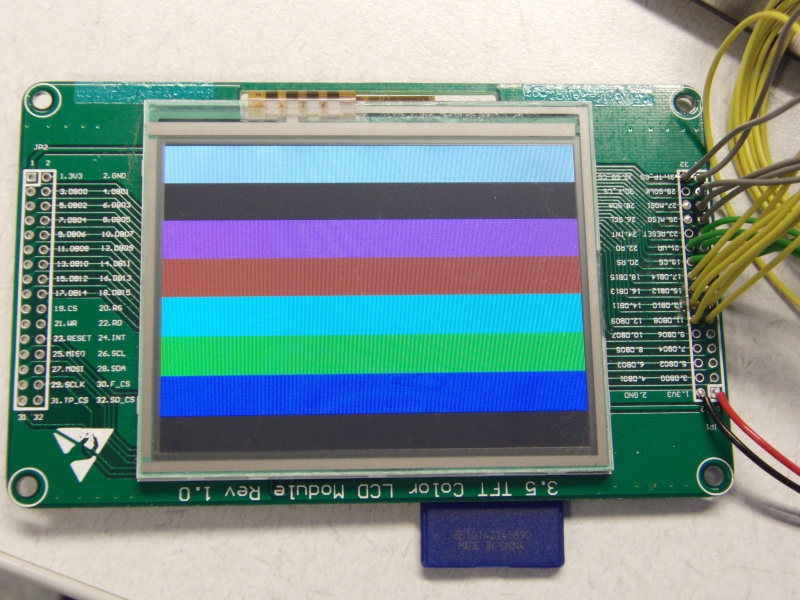
On ebay i found this very nice and cheap tft display .It contains a tft color screen with 320x240 pixels, touch-controller and Sd card reader.
The display controller used is the SSD2119 and for the touch controller they used ADS7843.
Demo is running on Atmel Avr M1284P @16Mhz with Bascom 1.12.0.0
Some Notes:
-- 320x240x16bits needs enormous amount of data and cpu power to get something on the screen, don’t expect live video @25fps. Take a look at the video to get an idea of the performance.
-- To get the display compatible with the Bascom 8bit BGC (Bascom Grapichs Color) files, the 8bits color are up-scaled to 16bits. Therefore the colors are maybe not always correct, you can adjust this in the look-up table.
-- The size of the BGC are limited to 255x255 pixels.
-- The 24bit colors of the BMP files are downscaled to 16bits by simply dropping the LSB.
-- Jumpers setting of the display board are a bit strange, make the soldering connection is a logic 0 and removing the solder is a logic 1.
-- The touch controller needs Polarity =low and Phase =0 for the spi communication, the Sd cards needs Polarity =high and Phase =1. To overcome this problem in the readtouch function’s the Polarity and Phase are changed at the beginning of the function and changed back at the end.
-- Display works on 3.3V so use a level converter or an AVR that can run on 3.3V.
-- Add the Spiin = 255 option to the Config Spi line in Config_mmc.bas if your using the touch and sd-reader, else it won’t work.
4373 Downloads
Syntax
Lcdtext string, x , y , fontset , forecolor , backcolor
Remarks
| String |
String to be displayed |
| x |
Constant or variable with x position. |
| y |
Constant or variable with y position. |
| fontset |
Fontset to be used to display the text |
| Forecolor |
RRRRRGGGGGGBBBBB |
| Backcolor |
RRRRRGGGGGGBBBBB |
This will show text on the lcd. It uses the Bascom FONT files for compatibility.
To add or remove fontsets modify these lines in the subroutine;
If Fontset = 1 Then Restore Font8x8
If Fontset = 2 Then Restore Font16x16
If Fontset = 3 Then Restore Font6x8
If Fontset = 4 Then Restore Font5x5
Sorry, but there was no better solution.
These are the name’s that you gave to the font, NOT the file-name if you don’t know the font name, open the font file in the font editor, and there it is, right on top.
Don’t forget to $Include your font files at the end of the program.
Syntax
Lcd_showpicture_bmp Filename, x , y
Remarks
| Filename |
Filename of Windows BMP file (24bpp) |
| x |
Constant or variable with x position. |
| y |
Constant or variable with y position. |
This will show Windows 24bpp BMP from the sd card. The 24bpp colors are downscaled to 16bpp.
Requires Avr-dos.
Syntax
Lcd_showpicture_sd Filename, x , y
Remarks
| Filename |
Filename of Bascom BGC file |
| x |
Constant or variable with x position. |
| y |
Constant or variable with y position. |
This will show Bascom BGC (Bascom Graphics Color) file from the sd-card. The 8bpp colors are up-scaled to 16bpp with the help of a look-up table. In this table you can adjust the colors if necessary.
Requires Avr-dos.
Syntax
Lcd_showpicture x , y
Remarks
| x |
Constant or variable with x position. |
| y |
Constant or variable with y position. |
This will show Bascom BGC (Bascom Graphics Color) file from the flash memory. The 8bpp colors are up-scaled to 16bpp with the help of a look-up table. In this table you can adjust the colors if necessary.
Important that you first Restore the picture, for example;
Restore Girl ‘FIRST restore you image before you can show it
Lcd_showpicture_sd “girl.bgc”, 150 , 10
Syntax
Lcd_line x1, y1 , x2 , y2 , color
Remarks
| x1 |
Starting horizontal location of the line. |
| y1 |
Starting vertical location of the line. |
| x2 |
Horizontal end location of the line. |
| y2 |
Vertical end location of the line. |
| color |
RRRRRGGGGGGBBBBB |
Draws a line on the lcd.
Syntax
Lcd_clear backcolor
Remarks
| backcolor |
RRRRRGGGGGGBBBBB |
Clears the lcd in an specified color.
Syntax
Lcd_pset x, y , color
Remarks
| x |
The x location. |
| y |
The y location. |
| color |
RRRRRGGGGGGBBBBB |
Set a pixel on the lcd.
Syntax
Lcd_Setcursor x, y
Remarks
| x |
The x location. |
| y |
The y location. |
Set the ram address (cursor) to the specified position.
Syntax
Write_data data16
Remarks
Write 16bit data to the lcd
Syntax
Write_Command Command
Remarks
Write 16bit command to the lcd
Syntax
Lcd_reset
Hardware lcd reset
Syntax
Lcd_init
Init the lcd
Syntax
Lcd_home
Set the ram address (cursor) to the home position
Syntax
A= Rgb16 rgb8
Remarks
| A |
16bpp RGB Word |
| rgb8 |
8bpp RGB |
Convert 8bpp color to 16bpp color.
Syntax
A= Readtouch_X
Remarks
| A |
12 Bit x position |
| rgb8 |
8bpp RGB |
Reads the X coordinates from the touchscreen.
Syntax
A= Readtouch_Y
Remarks
| A |
12 Bit y position |
| rgb8 |
8bpp RGB |
Reads the Y coordinates from the touchscreen.